Using Docker for local development (PHP)
- Objective
- Install Docker
- Start the container!
- Place your files in the directory and start developing!
Objective
Sometimes your FEUP server, gnomo.fe.up.pt, can misbehave or your area in particular be misconfigured (some students have been encountering such issues this year).
If you encounter Forbidden errors or any other mysterious stuff, but want to get some work done, try Docker to set a Apache + PHP Container in your local machine (you need Admin rights!).
Install Docker
Several instruction guides are here to help you install Docker on any platform.
Windows
Download the Docker Desktop Installer and run it.
Solutions to possible problems
Some possible errors have been listed here to point you towards a possible solution. Not everyone will encounter these errors.
- Lack of virtualization support
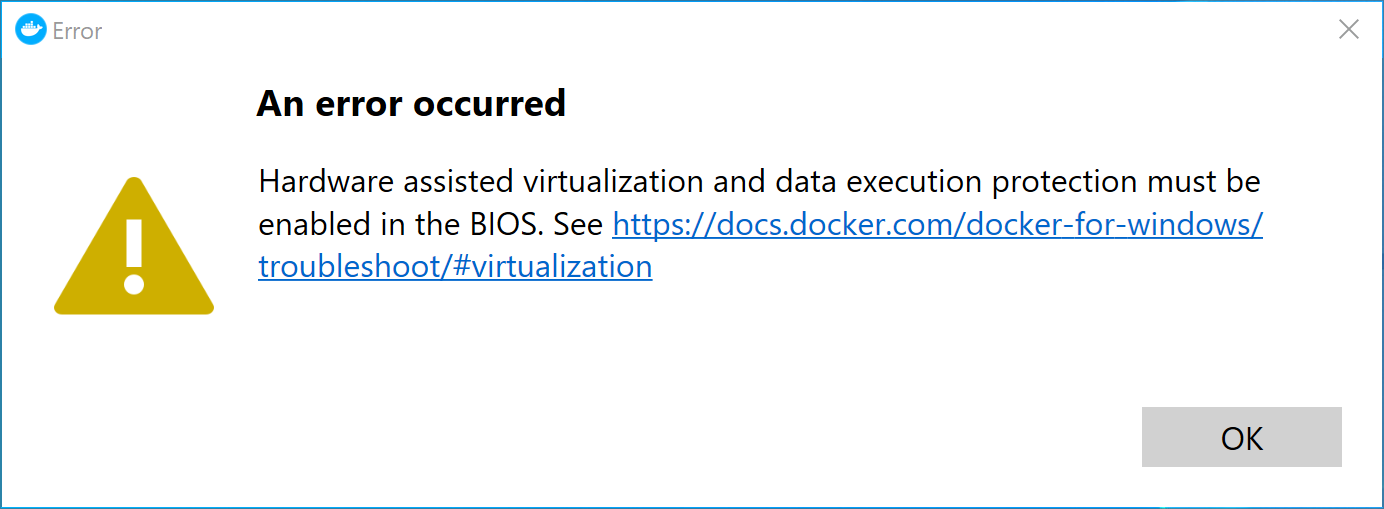
Remember to turn on Virtualization Support (or VT-x) on your computer’s BIOS/ UEFI (press Delete/F2 before Windows Starts) in order to run virtualization apps like Docker or a VM Hypervisor. See more here.
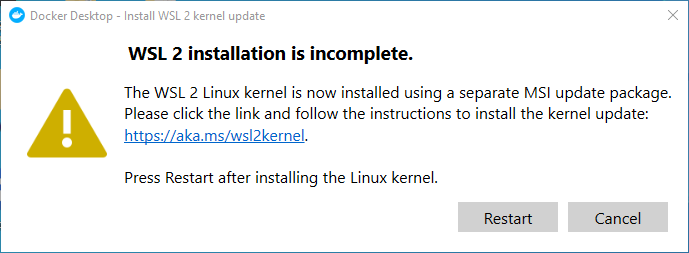
- WSL2 Linux Kernel message
If you get this when installing Docker, click the link in blue, follow the necessary instructions and then press the ‘Restart’ button.
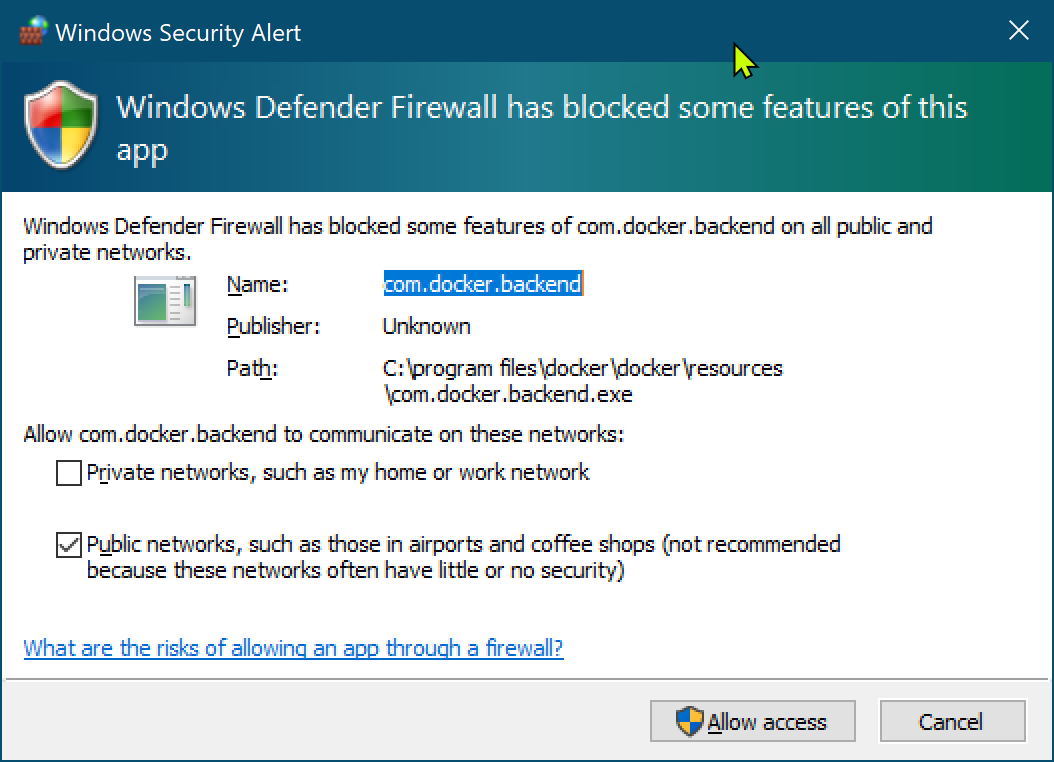
- Windows Firewall warnings
When Docker first starts on Windows, you may get this prompt. Select ‘Allow Access’.
macOS
Simply download the Docker Desktop Installer and run it.
Ubuntu Linux
I have compiled a script for easy installation.
- Fire up the Terminal,
- Run
sudo -iand type user password exitthe root command line- Paste the script found here in the Terminal.
Start the container!
Windows
Automated guide
- Download this zip file.
- Unzip the file into a folder of your choice.
- You will see a folder called
docker-scripts-for-windowsafter unzipping the file. - Inside
docker-scripts-for-windows, you will see a folder calledhtml, and 4 files:- 2 PowerShell Scripts (
.ps1extension) ← DO NOT TOUCH THESE - 2 Windows Batch Files (
.batextension) ← We will use these to start and stop our container
- 2 PowerShell Scripts (
- To start the container, run the
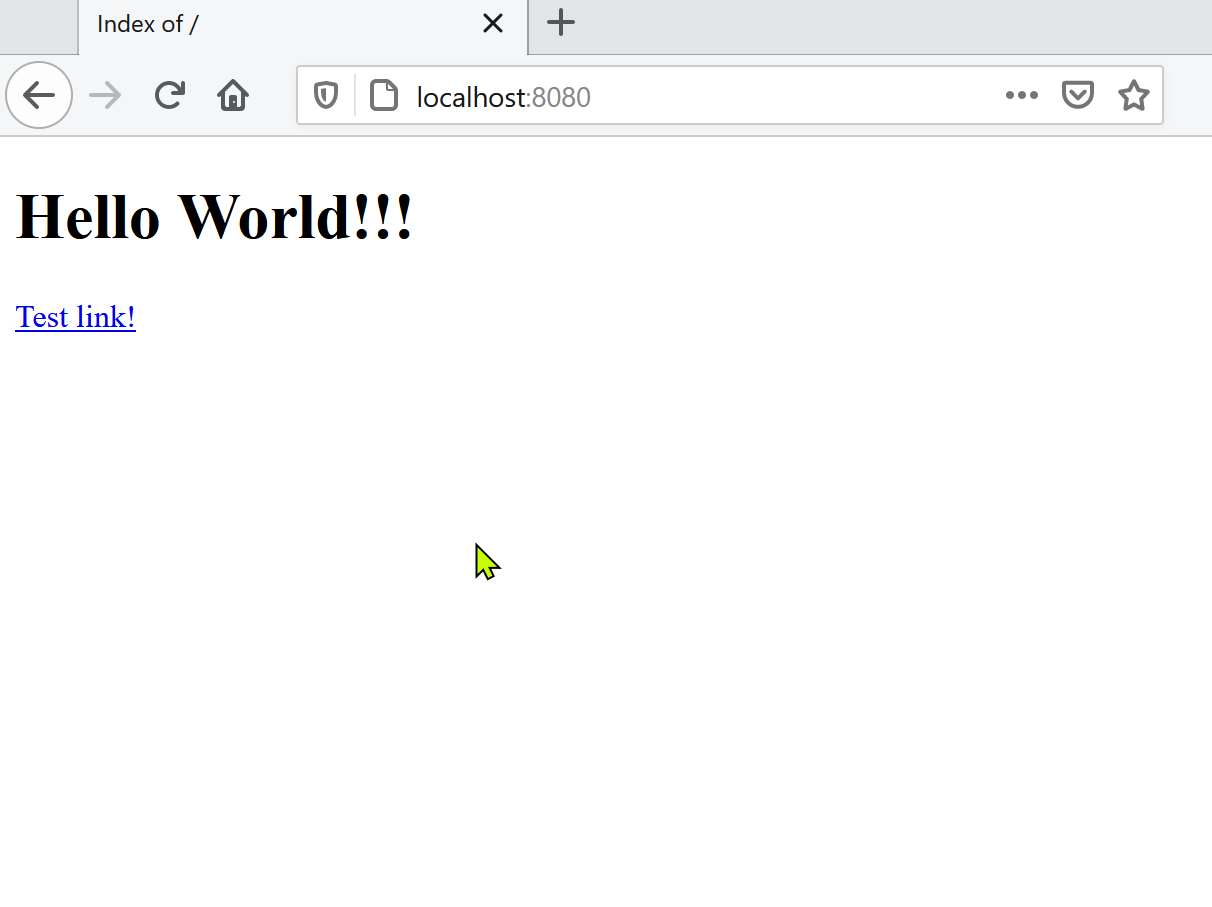
start-container.batfile. - Test your container, by navigating your browser to
http://localhost:8080. You should see this: - To stop the container, run the
stop-container.batfile.
Manual guide
- Create a new folder
htmlat the root of your hard drive for your website files:C:\html -
Open a terminal (
cmd.exe) with administrator privileges and run:1 2 3
```cmd docker run -d -p 8080:8080 -it --name=php -v C:\html:/var/www/html quay.io/vesica/php73:dev ```
(Optional) Create a .htaccess file inside the html folder
This is optional, but will allow the web server to generate nice file listings for easy navigation. To turn this on, go to the Server Root and create a new file called .htaccess, including the dot. The contents of the folder should be this:
Options +Indexes
After saving the file, point your browser to http://localhost:8080. You should see this:
Linux / Mac
- Create a new
htmlfolder for your web files:mkdir -p ~/html(~ means your home folder) - Open a terminal and run:
1
docker run -d -p 8080:8080 -it --name=php -v ~/html:/var/www/html quay.io/vesica/php73:dev
- (Optional) Create the .htaccess file inside the
~/htmlfolder. - Point your browser to http://localhost:8080.
Place your files in the directory and start developing!
From now on, whatever you put in the html Folder, should be accessible in the browser via the link http://localhost:8080.